The Future of Animal Production
The Future of Animal Production in Lebanon FAFS AUB Alumni Chapter
Contents Present imports and estimated local production of animal products. Consumption of animal products. Justifications to stimulate local production. Import duties on animal products. Measures to encourage investment in local production. Future outlook of local production based on implementation of above measures. Role of FAFS – AUB in Animal Production. Conclusion.
Imports & Estimated Production of Animal Products

Consumption of Animal Products
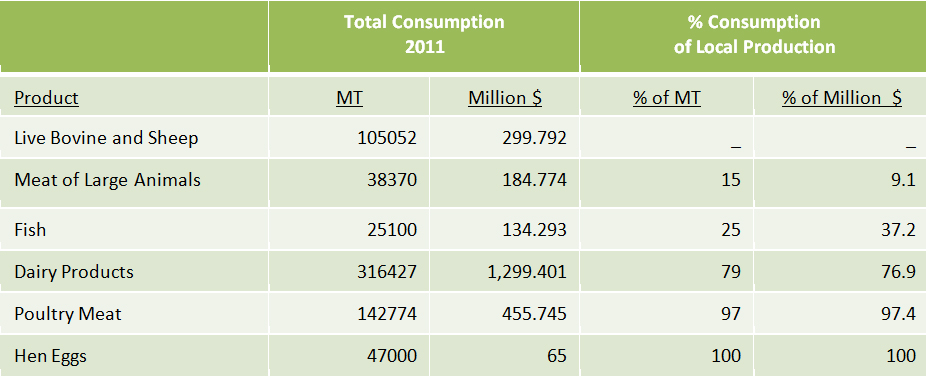
Justifications to Stimulate Local Production
- All industrialized countries subsidize agriculture: - Subsidies target all production including excess exported. - Subsidies distort the true value of the subsidized products destined for export. - Importation of subsidized products deter local production in the importing countries. - Direct subsidies violate the regulations of WTO in principle. - So far WTO trade agreements did not include agricultural and food products because the industrialized countries refuse to stop subsidizing agriculture. - EU subsidizes agriculture by 55 billion Euros/yr. - USA subsidizes agriculture by 180 billion USD/yr.
Justifications to Stimulate Local Production (Cont.)
- Two million Lebanese inhabitants live in rural areas (i.e. 50 % of the population), whose main livelihood depends on agriculture
- 25000 new Lebanese university and technical college graduates require jobs every year. The productive sectors may absorb 50 %.
- Diversification of economy is essential in any country.
- Lebanon cannot subsidize agriculture.
- World population is increasing at the rate of 2 % per annum, thus today’s surpluses for export may not be available for the importing countries soon.
Justifications to Stimulate Local Production (Cont.)
- Food security has become a revived subject of importance when designing the economic policies of most countries in the world.
- It is the duty of all governments to look after the interests of all people.
- The economic policies should be designed to serve all people. They are not meant to please other countries.
- Globalization does not stimulate investment unless there is a comparative advantage that would lead to exports.
- Lebanon lacks natural resources that help reduce its cost of production. Protection is the
Main Stimulus for Local Production
- Protection does not mean monopoly.
- Industrialized countries who claim open markets exercise protection by: - Increasing standards of quality. - Use non-tariff methods. - Resort to putting high tariffs on certain imports. - Refuse to sign bilateral free trade agreements on agricultural and food products.
- Industrialized countries subsidize exports: Turkey: 10 – 30 % China: 8 – 16 %
Protection is the Main Stimulus for Local Production (Cont.)
- WTO regulations allow developing countries to use protection to stimulate local production.
- The Arab Free Trade Agreement fully implemented in 2004 did not improve bilateral trade. It has been abused allowing re-exporting non-Arab products as being of Arab origin.
- Protectionist policy relieves Lebanon from subsidizing the production of tobacco and wheat and the export of certain fresh vegetables and fruits that cost 100 million USD/yr.
- Abiding by the dictated economic policies of reduction of import duties has resulted in closing many industries in Lebanon such as: - Shoes, clothing and ceramics. - Furniture, medicines and glass. - Many agricultural products such as lentils, beans, chick peas, sugar beet, barley, corn, etc.
Protection is the Main Stimulus for Local Production (Cont.)
- Subsidy has kept production of wheat and tobacco alive.
- Monopoly has kept the electric cables and cement industries alive.
- Prices of imported goods often increase. Governments thus justify the increases of prices of such goods. Why not accept increasing prices by import duties to stimulate local production.
- Protection is practiced in Lebanon: - The syndicates of engineers, doctors, lawyers and pharmacists are protected. - The gas stations are protected. - The pharmacies are protected. - MEA is highly protected. - Exclusive agencies are protected.
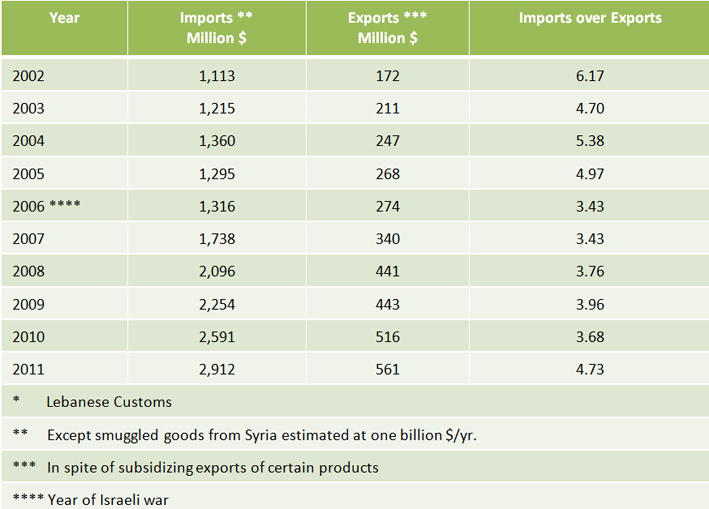
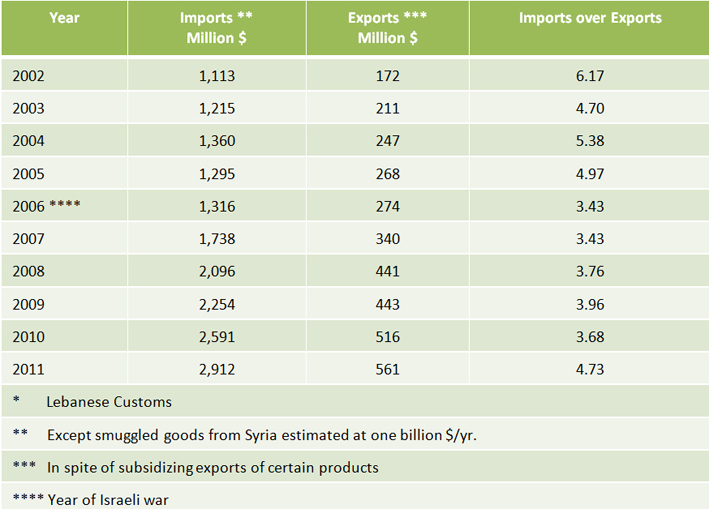
Imports & Exports of Agricultural Goods *
Import Duties on Animal Products
Import Duties on Animal Products

Effect of Import Duties on Local Production of Animal Products

- Targets: - Reduction of trade imbalances. - Reduction of imports. - Encouraging investments in productive sectors. - Creating jobs and reducing immigration.
- Measures: - Revision and amendment of all bilateral and group trade agreements. - Impose effective import duties on all available products that may possibly be produced
- locally. - Negotiate entrance to WTO using the revised and stepped up import duties. - Stop subsidizing wheat and tobacco. - Stop smuggling from Syria. - Step up security, clean up the judiciary system and stop corruption.
- All above measures require legislation and not financing.
Future Outlook based on above Measures
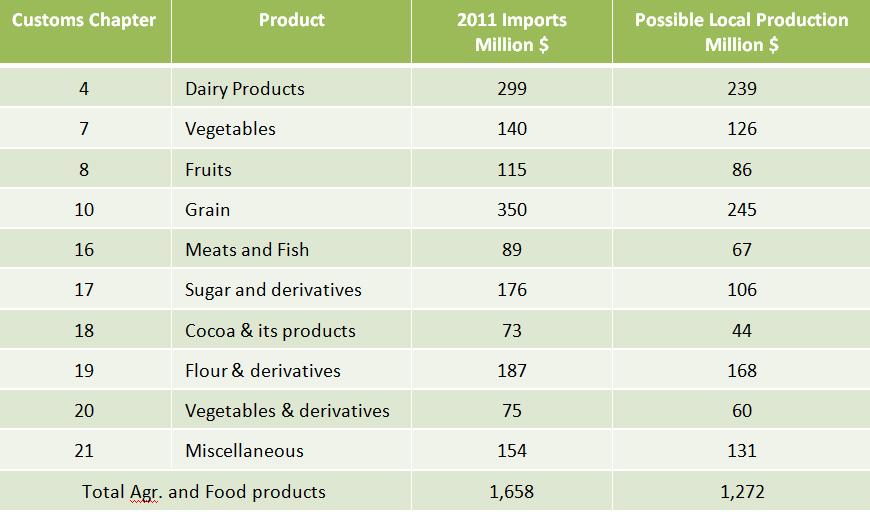
Results of above Measures
- The value of agricultural and food items that may replace imports amount to 1.3 billion USD or 77 %.
- Investment needed to achieve the above is approximately 3 billion USD.
- Jobs created by such investment is 25000.
- Protecting local production from unfair competition due to subsidies and lower cost of production.
- Diversification of production instead of directing it to the subsidized products.
- Reduction of imports and thus reduction of export of hard currency.
- Encouraging contract farming.
- Keeping farmers in their local areas.
Results of above Measures (Cont.)
- Creating jobs for agricultural graduates.
- Creating new opportunities for supporting businesses.
- Relieving the government from subsidizing exports of certain agricultural products.
- Leaving all other issues related to deciding on types of crops or animals to produce or raise, marketing, financing, exporting, etc. to the private sector to decide within a true local competitive environment.
The Role of FAFS in Animal Production
- FAFS-AUB graduates have been instrumental in enhancing animal production in Lebanon.
- The market looked highly at FAFS-AUB graduates.
- FAFS-AUB graduated did not have any difficulty in finding good jobs as soon as they graduated.
- Multinational companies were always eager to employ FAFS-AUB graduates and give them regional responsibilities.
The Role of FAFS in Animal Production (Cont.)
- The job market, small as it is in Lebanon, still considers the superiority of the academic standard of FAFS-AUB graduates.
- The future of jobs for FAFS-AUB graduates depends on the Lebanese economic policy vis-à-vis the local animal production as detailed in this presentation.
- The academic basis of FAFS-AUB is undoubtedly flexible and capable to answer the market demand.
Negative Consequences in case of not Implementing suggested Measures
- Increase of imports of food items to 85 % of local needs.
- Increased movement from rural to urban areas.
- Increased unemployment.
- Increased immigration of specialties (brain drain).
- Keeping Lebanon as an underdeveloped country.
Conclusion
- Trade agreements are not an end but a means to serving the interest of the people, all people.
- Governments are responsible to reduce unemployment and inflation via appropriate legislations.
- Governments should not hesitate to amend trade agreements.
- Loss of certain exports as result of adopting a protectionist policy is happening anyway as a result of our high cost of production.
- All governments since 1992 up till now have failed to improve the Lebanese economy.
- Hesitation in adopting protectionist measures towards the productive sectors is to be considered as an act of treason.
Thank you, Musa Freiji Beirut, Nov. 16, 2012